Incoterms F Group (FOB/FCA/FAS)
Overview







What You Can Gain from This Topic
- Review of Incoterms
- F Group’s Characteristics
- FOB, FCA, and FAS Delivery Points
- How to Prepare an Invoice
Review of Incoterms
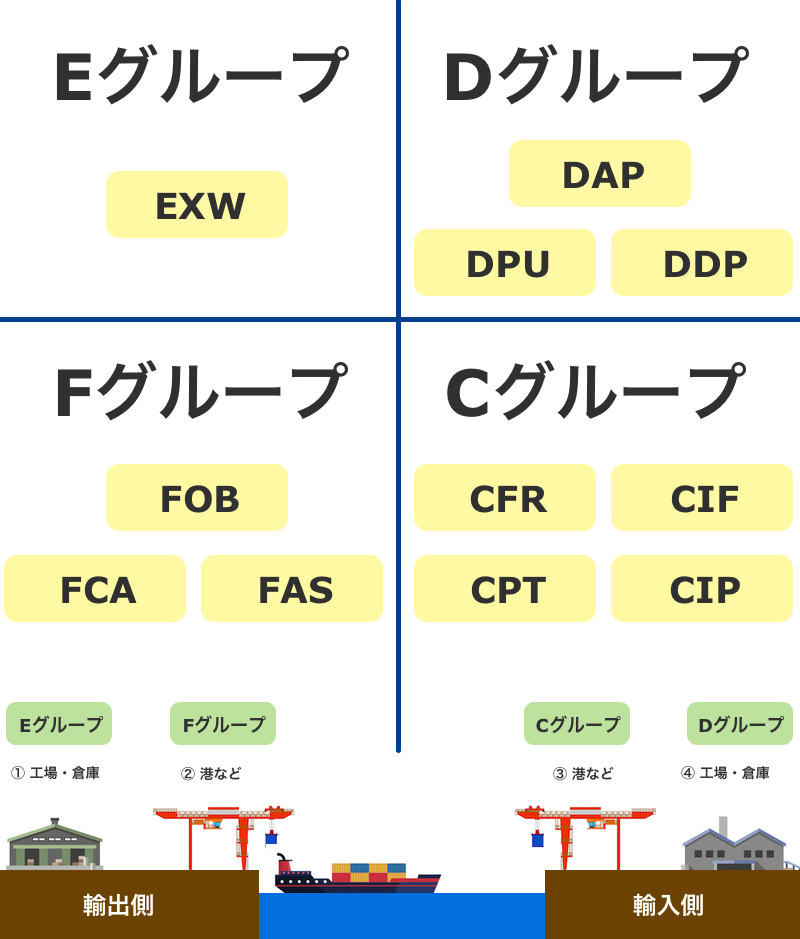
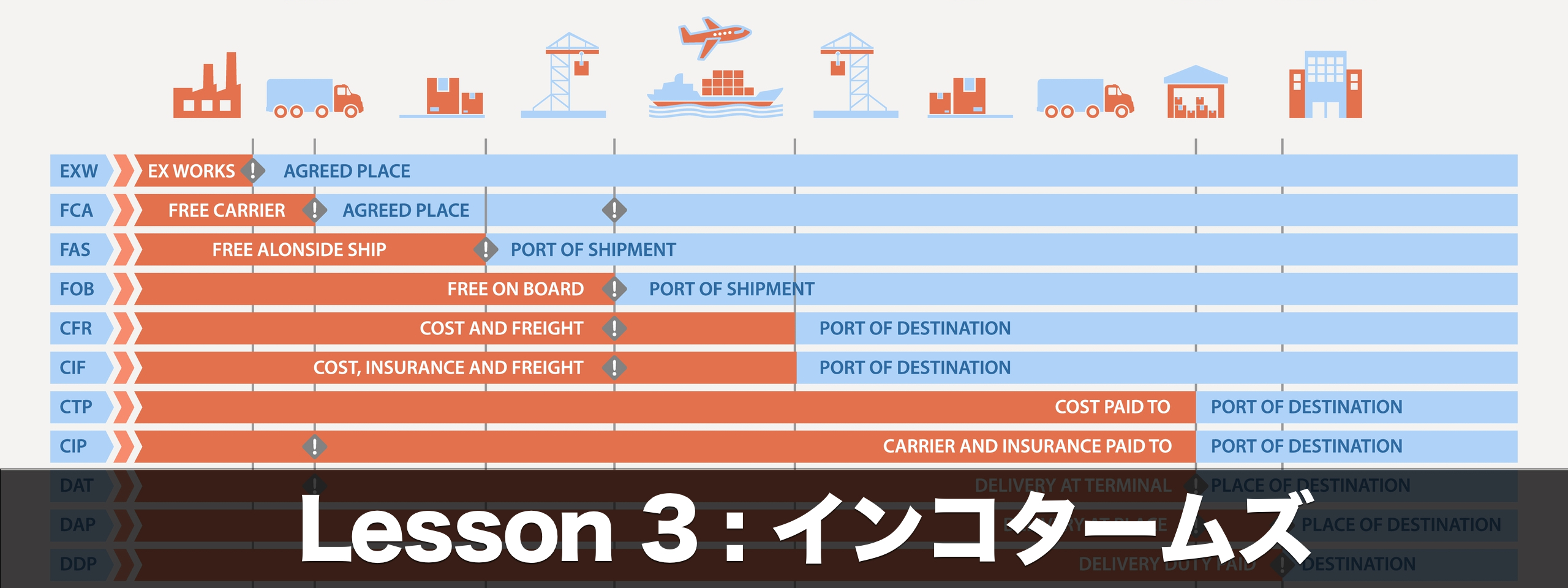
Incoterms are broadly divided into four groups, as explained in the previous topic.
In the F Group, the cargo is handed over from the exporter to the transporting company designated by the importer at a specific location on the export side.



F Group’s Characteristics
F Group has three trading terms as the following:
・FOB (Free on Board)
・FAS (Free Alongside Ship)
・FCA (Free Carrier)
The three trading terms in the F Group are formally distinguished based on the modes of transportation.
・Terms for conventional ship transportation: FOB, FAS
・Terms for container ship transportation: FCA


Conventional Ship
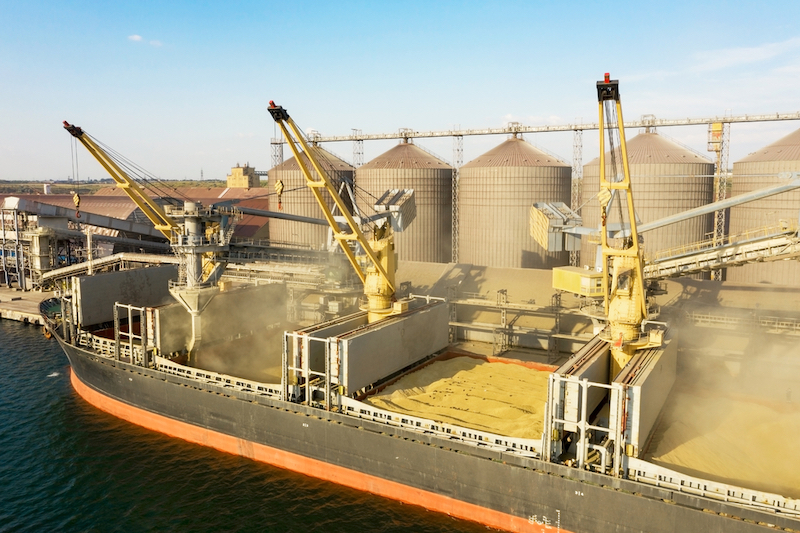

A conventional ship (or bulk carrier) is a vessel designed for transporting commodities such as grain, scrap, sugar, and large cargo by directly loading them onto the ship.

Container Ship
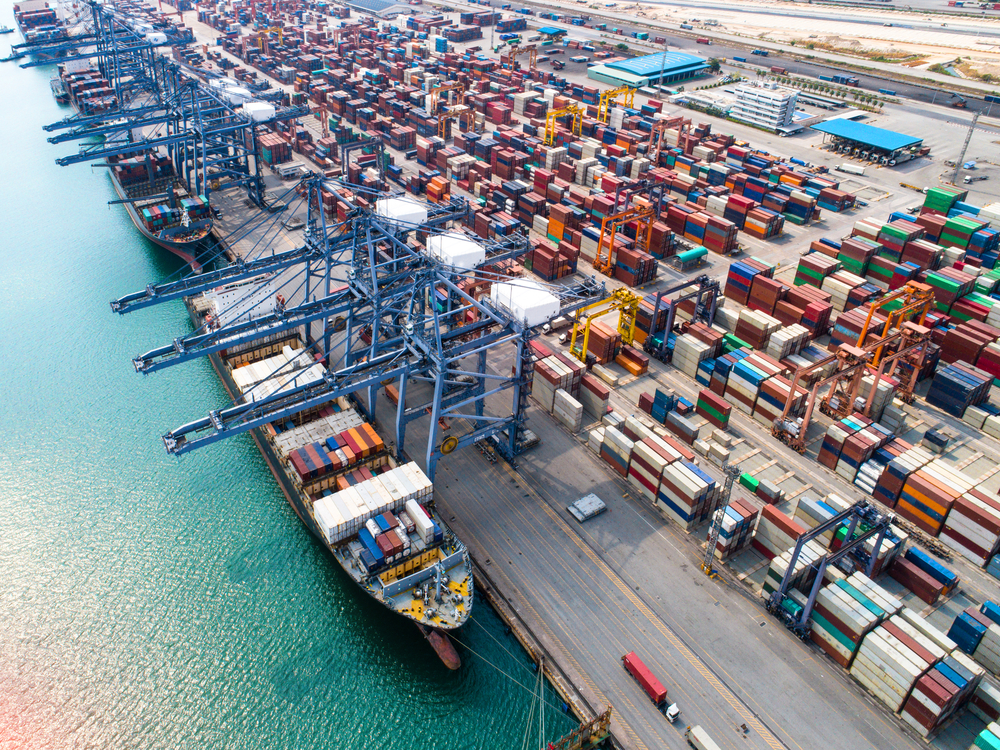

A container ship is a type of cargo ship specifically designed for the efficient transport of standardized cargo containers.


FOB in Practical Work
Although the above is the official rule, FOB is used as follows practically.
・Terms for container ship transport: FCA
Practical Work:
・Terms for conventional ship transport: FOB, FAS
・Terms for container ship transport: FOB, FCA





FOB, FCA, and FAS Delivery Points
The delivery point is the place where the burden of cost and risk shifts from exporter to importer.

FOB

The delivery point for FOB (Free On Board) is typically when the goods are loaded onto the designated vessel at the specified port of shipment.
FCA

The delivery point for FCA (Free Carrier) is when the goods are delivered to the carrier nominated by the buyer at the seller’s premises, such as a container terminal or warehouse at the export site.
FAS

The delivery point for FAS (Free Alongside Ship) is when the seller delivers the goods alongside the named vessel at the specified port.

Difference between FOB and FCA

Understanding the difference between FOB and FCA can help you manage your risk. It’s important to consider the perspectives of both the importer and exporter.
In the exporter’s position, FCA has less risk than FOB. This is because the delivery point for FOB is after the cargo is loaded onto the vessel, whereas FCA occurs before vessel loading.






How to Prepare Invoice
In the case of FOB, the unit price includes transportation costs to the export port.
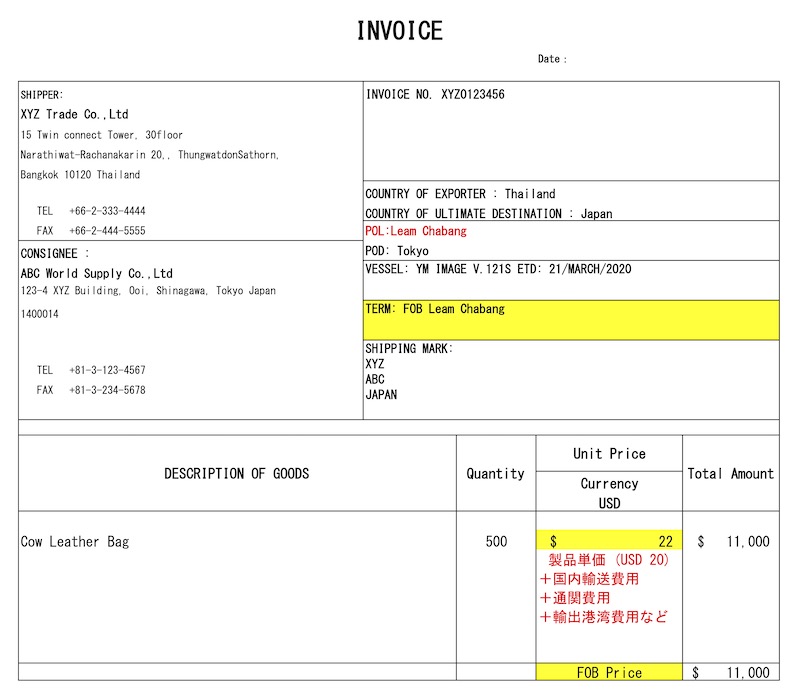
The transportation cost is typically prorated based on quantity and added to the unit price.

Summary
In Incoterms F Group, the delivery point is at the port of shipment.
In international trade, the point at which the risk and cost of transporting goods is transferred from the exporter to the importer varies depending on the terms of sale.

Enhanced Learning with Videos
Test Yourself
Reinforce your understanding of this topic by working through the exercises. Attempting the exercises without referring to the material as much as possible is advisable.




