10-2. Customs Procedures in Maritime Export

Overview





Learning Points
- Customs Procedures in Maritime Export
- Required Documents
Export Customs Clearance Procedure
Customs clearance for maritime exports proceeds as follows.
1. Preparation for customs procedures
2. Confirming if the cargo requires export permission or approval by competent agencies
3. Submitting the export declaration
4. Transporting the goods to the bonded area
5. Loading onto the vessel
6. Sending Shipping Advice (SA) to the importer



1. Preparation
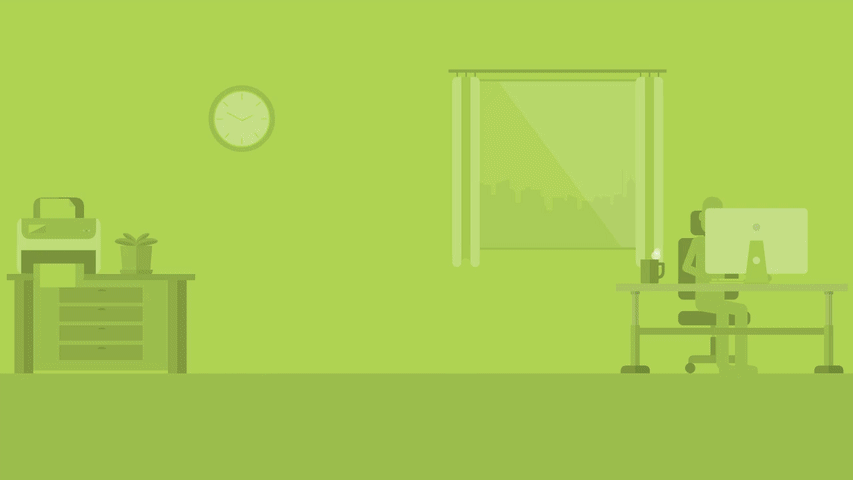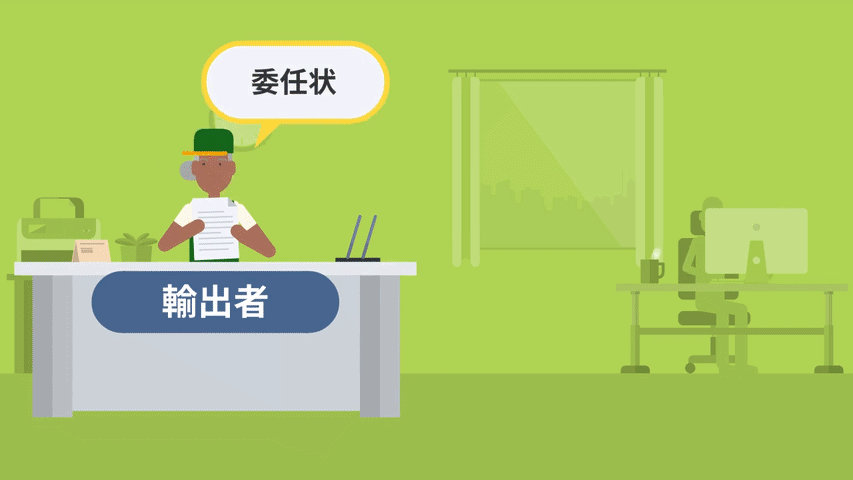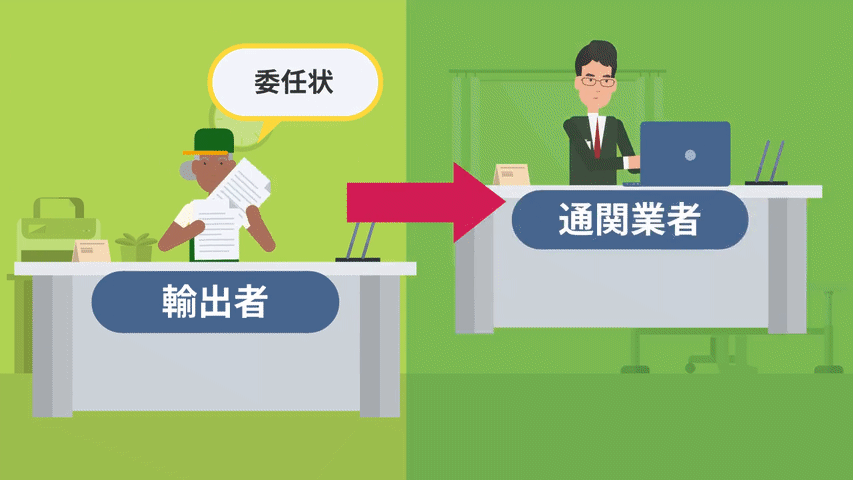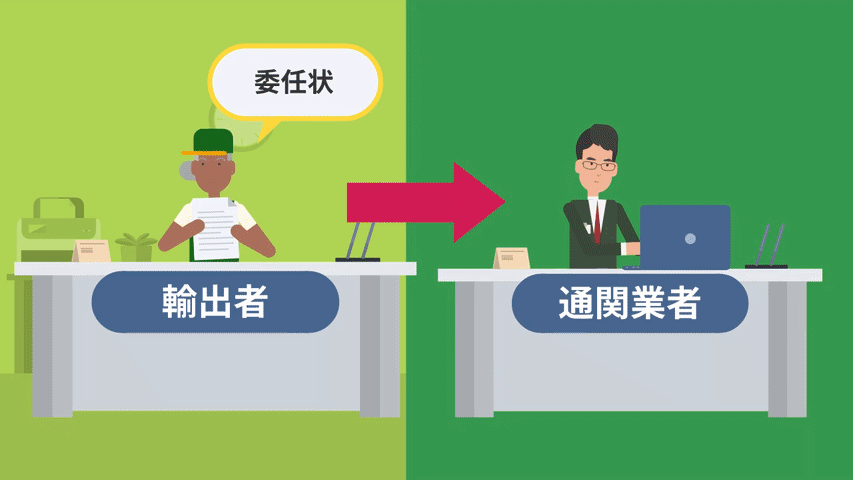
Exporters entrust customs clearance to a customs broker.


Required Documents
・Shipping Instruction
・Invoice
・Packing List
・Product catalog (MSDS, etc.)
・Other required permits


Shipping Instruction (S/I)
A Shipping Instruction is a document the shipper provides to the shipping company or freight forwarder.
It contains detailed instructions regarding the shipment of goods, including information about the cargo, its destination, and how it should be handled.

Invoice
Packing List
A Packing List (P/L) is a document that provides information on the packaging method, weight, size, and shipping marks on cargo cases. This is also used for customs clearance.

Catalogs or MSDS
Shippers may need to submit catalogs and MSDS when exporting a product for the first time.
MSDS, an abbreviation for Material Safety Data Sheet, contains information about such as the following:
- The material
- Handling precautions
- Applicable regulations
- Other details related to product safety
- Shipping Instruction
- Invoice
- Packing List
If necessary, prepare the following also.
- Catalogs
- MSDS


2. Verifying if Export Permission/Approval is Needed

Before making a declaration, confirming whether the cargo requires permission or approval in the exporting country is essential.
If the goods necessitate permission or approval, the shipper must complete the application form and gather the necessary documents.


3. Submiting the Export Declaration

After checking the shipping documents, customs brokers proceed with export declarations on behalf of the exporter.
The methods for declarations vary by country. The Automated Export System (AES) is utilized in the United States. Similarly, an online system known as NACCS (NACCS) is used in Japan.


Two Deadlines
When submitting export declarations, paying attention to the two cutoff dates below is important.
- Documentation cutoff date
- CY/CFS cutoff date
The Document Cutoff Date is the deadline for submitting shipping documents. The CY/CFS cutoff date is the deadline for cargo delivery.

24-Hour Rule
The “24-hour rule” is a regulation in international shipping, particularly related to the advance notification of cargo information to customs authorities.
In this regulation, customs brokers must submit cargo information to the shipping company at least 24 hours before goods are loaded on the main vessel.
Below are three representative 24-hour rules:
- North America 24-Hour Rule
- EU 24-Hour Rule
- China 24-Hour Rule

4. Bringing Goods into Bonded Areas

The exporter transports the goods to a bonded area. The goods are stored there until the export permit is granted.
Where the goods are brought in depends on whether it’s FCL or LCL. FCL is delivered to the container yard (CY), but LCL is delivered to the Container Freight Station (CFS).
LCL cargo brought into the CFS is consolidated with goods from other exporters and, after loading into one container, is transported to CY.

5. Loadeding on the Vessel

Once the export permit is obtained, the goods are loaded onto the main vessel from the bonded area and depart. After departure, the shipping company issues the Bill of Lading (B/L).
If the shipper/consignee loses the B/L, it can cause issues with import customs clearance. So, it’s crucial to be extremely careful and avoid any mishandling of it.

6. Sending S/A to the Importer

After customs clearance, the exporter sends the complete documents to the importer as Shipping Advice (S/A) before the cargo arrives at the importing location.

Summary
In this topic, we provided an overview of the general flow of maritime exports. The detailed procedures vary by country.
To ensure a smooth export process, it is crucial to prepare the required documents thoroughly. Additionally, pay attention to handling the Bill of Lading (B/L).


Take the Test
Reinforce your understanding of this topic by working through the exercises. Attempting the exercises without referring to the material as much as possible is advisable.




